Definition Of Diffusion Disease

1 to describe the spatial.
Definition of diffusion disease. The tendency of a gas or solute to pass from a point of higher pressure or. Diffusion mri is one of the most interesting and promising techniques available today to explore neurological diseases. Mountains bodies of water political and economic boundaries may also limit the spread of disease. This type of diffusion was recognised in the recent h1n1 flu virus that had its source in mexico.
Benedetta bodini olga ciccarelli in diffusion mri second edition 2014. In various diseases e g interstitial fibrosis pulmonary collagenosis there occur an increase in resistance to diffusion of o 2 from alveoli to the capillaries. How to use disease in a sentence. This kind of proliferation is known as spatial diffusion.
Co 2 is much more soluble than o 2 and its diffusibility is at least 20 times higher than. Relocation diffusion is a spatial spread process whereby the disease leaves the areas in which it originated as it moves into new areas. This chapter shows that it can be successfully applied to several disorders of the central nervous system affecting both the brain and spinal cord. In geography the term diffusion refers to the spread of people things ideas cultural practices disease technology weather and other factors from place to place.
Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific symptoms and signs. According to rytokonen the goals of disease mapping are. As the disease expands into new areas it is likely to weaken. An example of relocation of disease can be seen.
Failed verification a disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. It implies that a disease spreads or pours out from a central source. The three main types of this phenomenon are expansion diffusion stimulus diffusion and relocation diffusion. Diffusion of co 2.
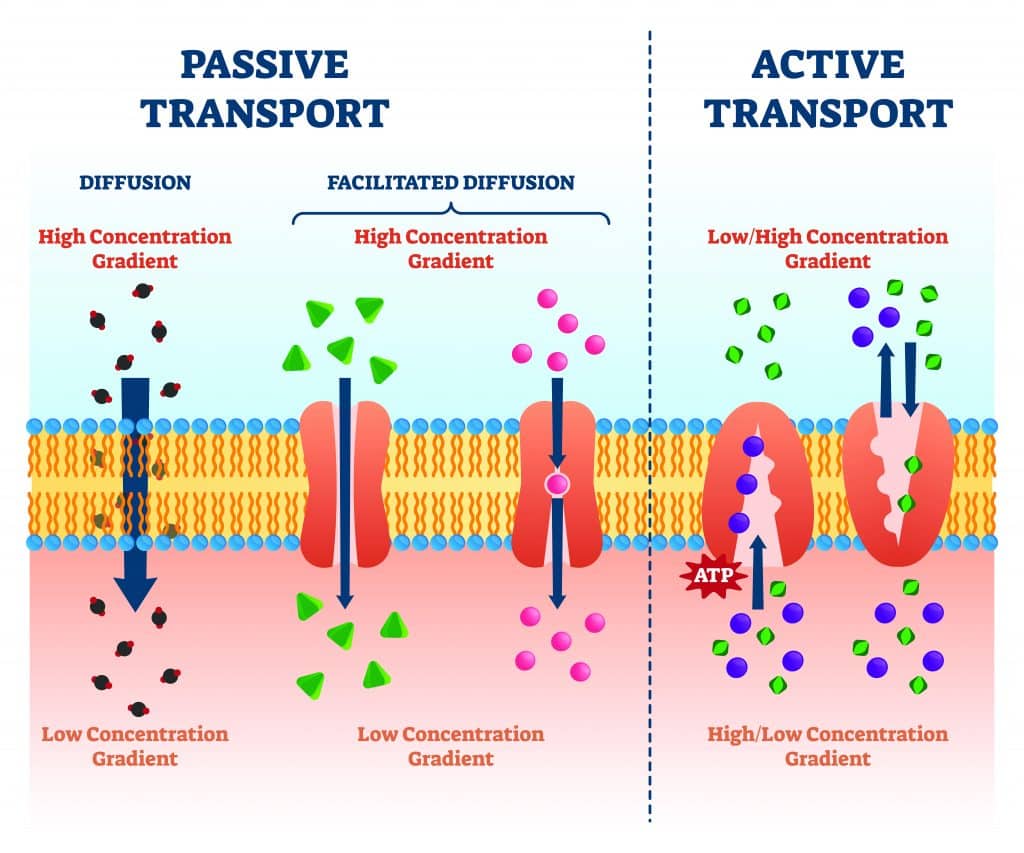
Diffusion the movement of a phenomenon from one location to another. Diffusion description of diffusion. A major mechanism of biological transport. Disease definition is a condition of the living animal or plant body or of one of its parts that impairs normal functioning and is typically manifested by distinguishing signs and symptoms.
The network diffusion model does not support the retrogenesis hypothesis that ad is a wm specific disease and is caused by demyelination of late myelinating fiber pathways bartzokis 2004. The idea of showing the spread of disease using a diffusion pattern is relatively modern compared to earlier methods of mapping disease which are still used today. Disease diffusion refers to the spread of a disease into new locations barriers to diffusion some physical features act as a barrier towards diffusion including. These diseases together constitutes alveolo capillary block syndrome.