Definition Of Glucose Homeostasis

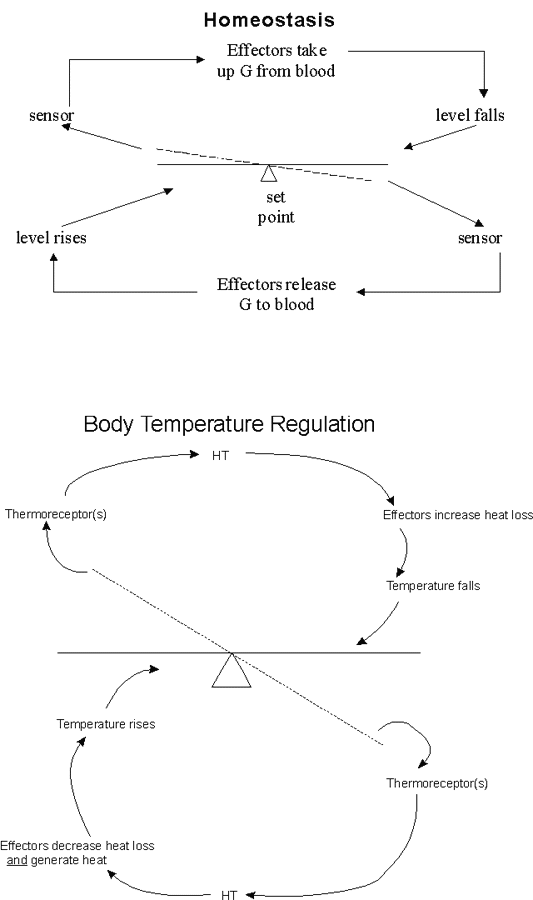
The word homeostasis d of the blood glucose affecting factors listed above diet plays the largest role.
Definition of glucose homeostasis. Glucose homeostasis in mammals is primarily maintained through glucose uptake in organs in the fed state and production of glucose by the liver during fasting. Secreted by the pancreas in response to elevated blood glucose following a meal. When the blood glucose level rises after a meal the liver removes. The low blood concentrations of glucose can cause seizur es loss of.
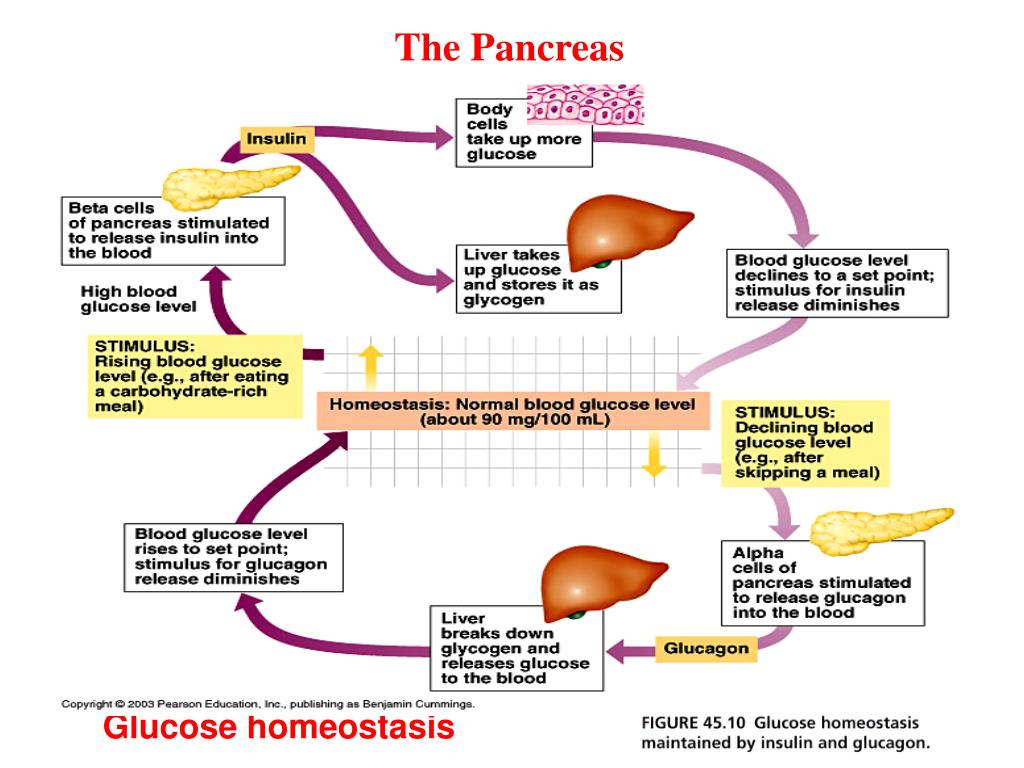
Insulin lowers blood glucose by increasing glucose uptake in muscle and adipose tissue and by promoting glycolysis and glycogenesis in liver and muscle. The body is able to. The balance of insulin and glucagon to maintain blood glucose. Homeostasis is the regulation of conditions in the body such as temperature water content and carbon dioxide levels.
The pancreas produces insulin which allows the transport of glucose into the cell. Our liver plays a vital role in blood glucose homeostasis. Homeostasis definition homeostasis is an organism s process of maintaining a stable internal environment suitable for sustaining life. People with diabetes may need to take insulin injections to control their high blood glucose.
Glucose homeostasis relies on the balance and interactions of two hormones insulin and glucagon to maintain a healthy blood glucose level. As far peripheral utilization is concerned it is not confined to any tissue or organ. Immediately after a meal insulin signals the liver to attenuate glucose production arresting both glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis and instead to focus on glycogenesis. Homeostasis definition homeostasis is the state of steady internal chemical and physical conditions maintained by living systems.
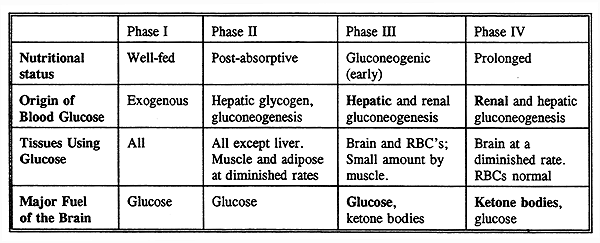
3 1 definition of glucose homeostasis most tissues and organs need glucose constantly as an important source of energy. Blood sugar regulation is the process by which the levels of blood sugar primarily glucose are maintained by the body within a narrow range this tight regulation is referred to as glucose homeostasis insulin which lowers blood sugar and glucagon which raises it are the most well known of the hormones involved but more recent discoveries of other glucoregulatory hormones have expanded. Whether old or young. When not enough insulin is available in the body the amount of glucose the cells are able.