Definition Of Isotope Of Lithium

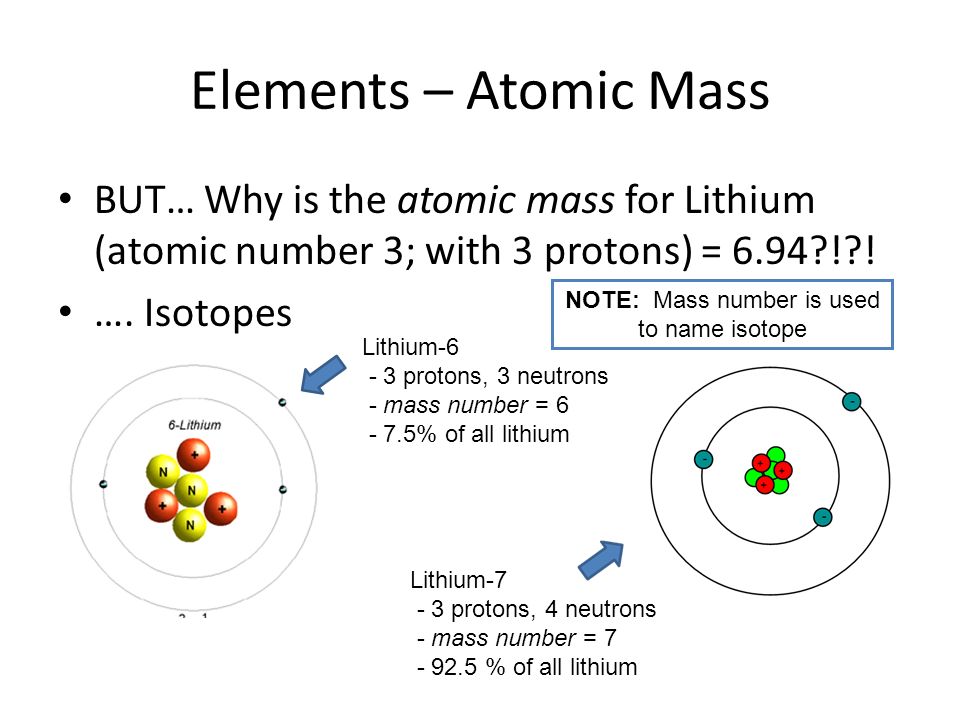
Lithium 6 is valued as a source material for tritium production and as a neutron absorber in.
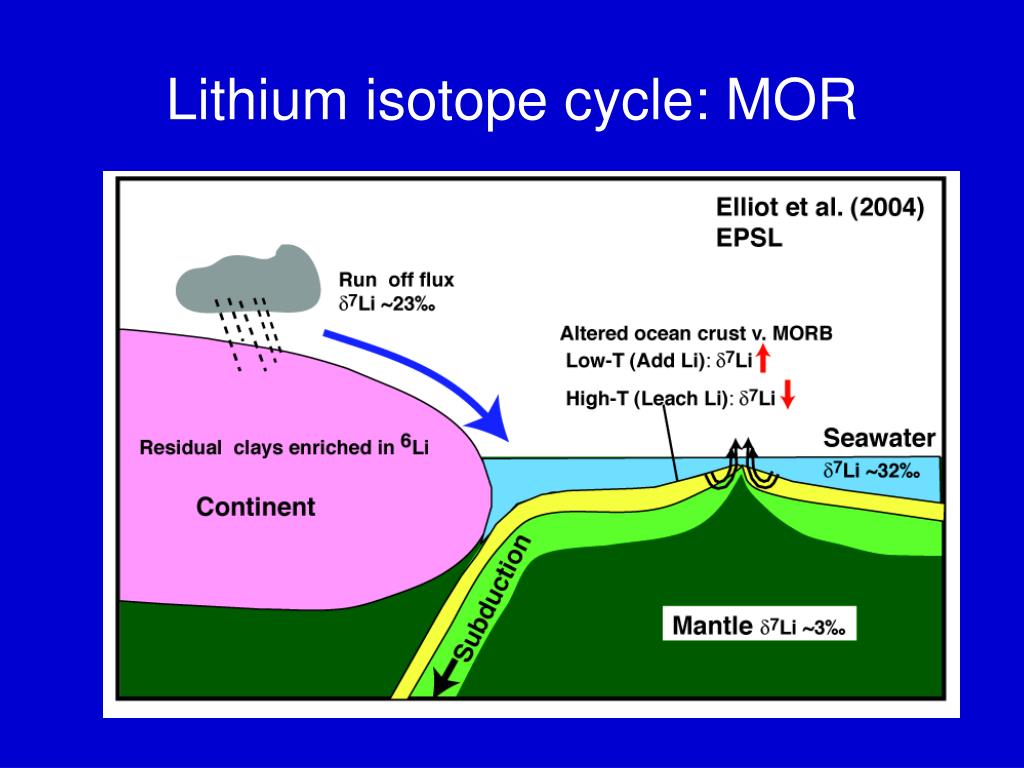
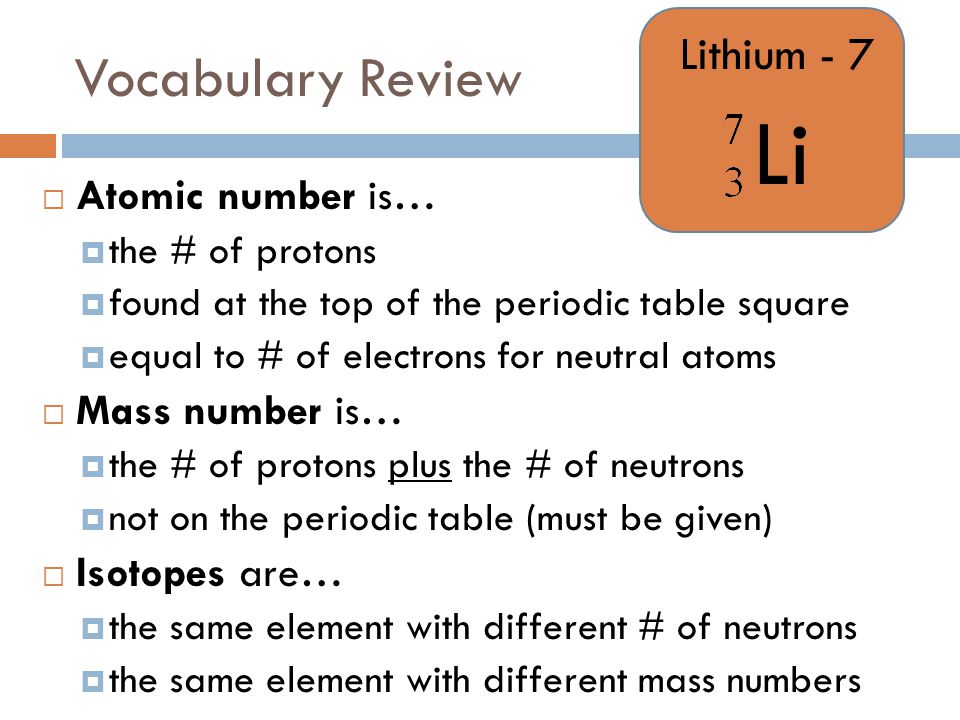
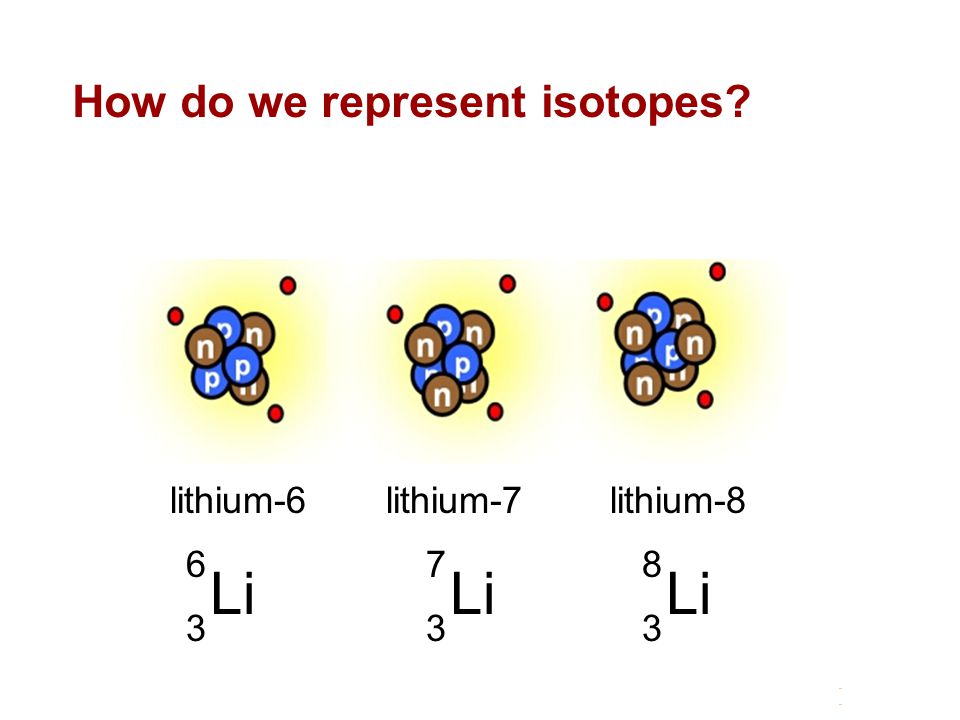
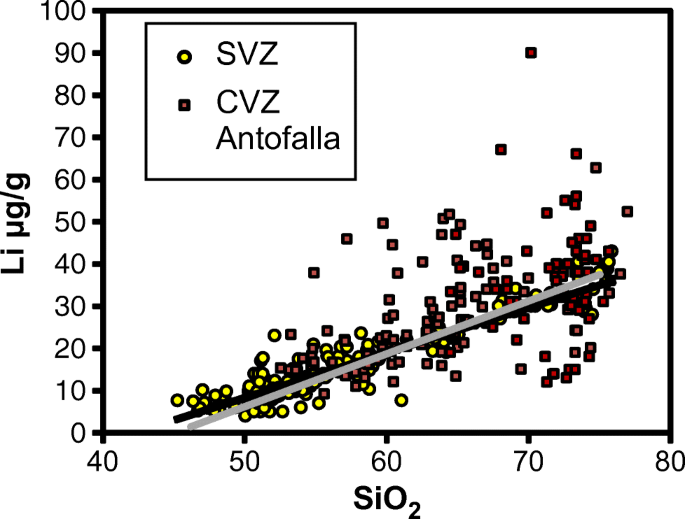
Definition of isotope of lithium. The large relative mass difference between the lithium isotopes 7 li 92 5 and 6 li 7 5 leads to isotopic fractionations of li during equilibrium and kinetic reactions in earth systems substantial 20 30 δ 7 li differences exist between natural waters and rocks. It is the shortest lived isotope of lithium. The nuclide concept referring to individual nuclear species emphasizes nuclear properties over chemical properties whereas the isotope concept grouping all atoms of each element emphasizes chemical over nuclear. Lithium 7 is by far the most common isotope of natural lithium making up about 92 5 percent of the atoms.
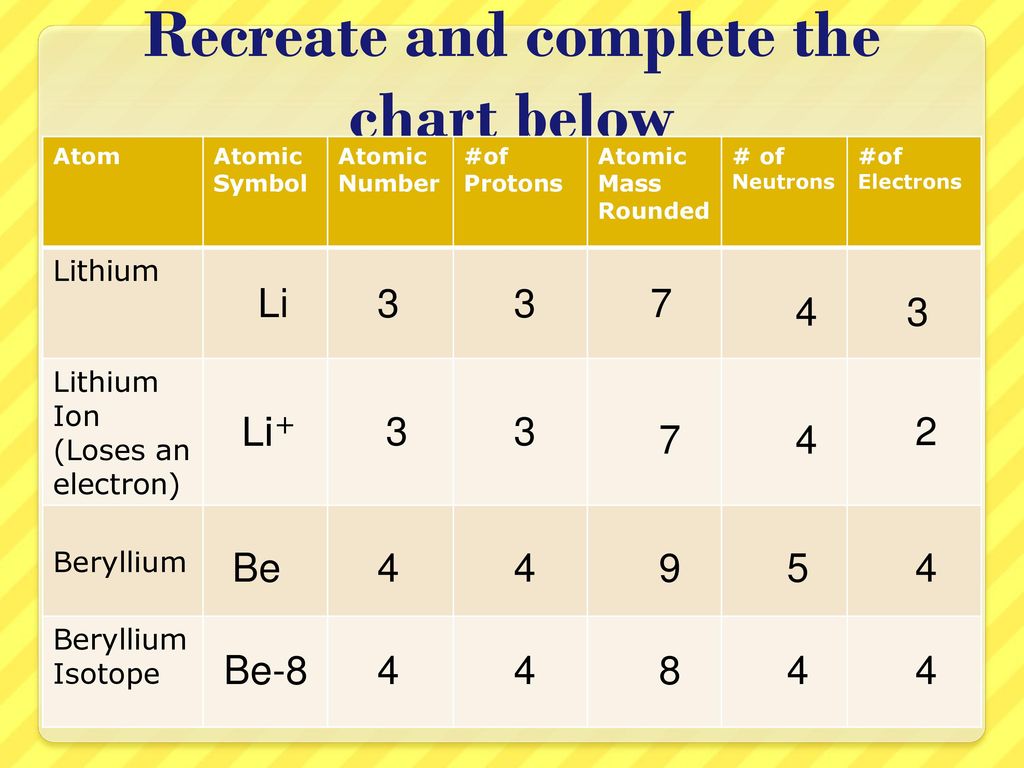
Isotope definition is any of two or more species of atoms of a chemical element with the same atomic number and nearly identical chemical behavior but with differing atomic mass or mass number and different physical properties. As elements are categorized by the number of protons in the. It s all in the neutrons. Lithium ions replace magnesium or iron in certain octahedral locations in clays and lithium 6 is sometimes preferred over lithium 7.
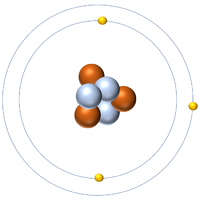
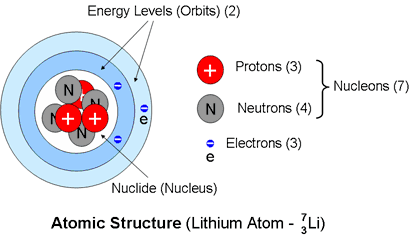
Any lithium 7 atom contain three protons four neutrons and three electrons and it is a boson which means that its total atomic spin is an integer usually zero. Every chemical element has one or more isotopes. Isotope one of two or more species of atoms of a chemical element with the same atomic number and position in the periodic table and nearly identical chemical behaviour but with different atomic masses and physical properties. A nuclide is a species of an atom with a specific number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus for example carbon 13 with 6 protons and 7 neutrons.
Mafic igneous rocks from all tectonic settings range in δ 7 li from 2 to 6 suggesting a uniform mantle. Li 7 accounts for about 92 5 percent of natural lithium. Isotope definition any of two or more forms of a chemical element having the same number of protons in the nucleus or the same atomic number but having different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus or different atomic weights. Isotopes are variations of atoms that classify as the same element.
It decays by proton emission and has a half life of 9 1 10 23 s. Because of lithium s nuclear properties it is less abundant in the universe than helium beryllium carbon nitrogen or oxygen. Lithium 6 is an important isotope in nuclear physics because when it is bombarded with neutrons tritium is produced. Lithium 7 is the second stable lithium isotope and the most abundant.
This results in some enrichment of lithium 7 in geological processes. There are 275 isotopes of the 81 stable elements in addition to over 800 radioactive isotopes and every element has known isotopic forms. An atom is first identified and labeled according to the number of protons in its nucleus.