Definition Of Isotope Ratios

The mass of a neutron is almost identical to that of a.
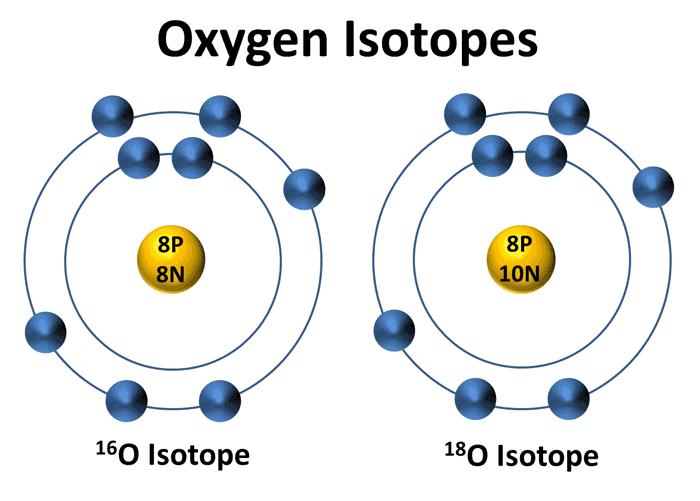
Definition of isotope ratios. Carbon 12 and carbon 14 are both isotopes of carbon one with 6 neutrons and one with 8 neutrons both with 6 protons. Wikipedia definition isotope analysis is the identification of isotopic signature the abundance of certain stable isotopes and chemical elements within organic and inorganic compounds. There are 275 isotopes of the 81 stable elements in addition to over 800 radioactive isotopes and every element has known isotopic forms. It represented 3 7 and 12 at 20 cm for treat92 88 and 69 respectively.
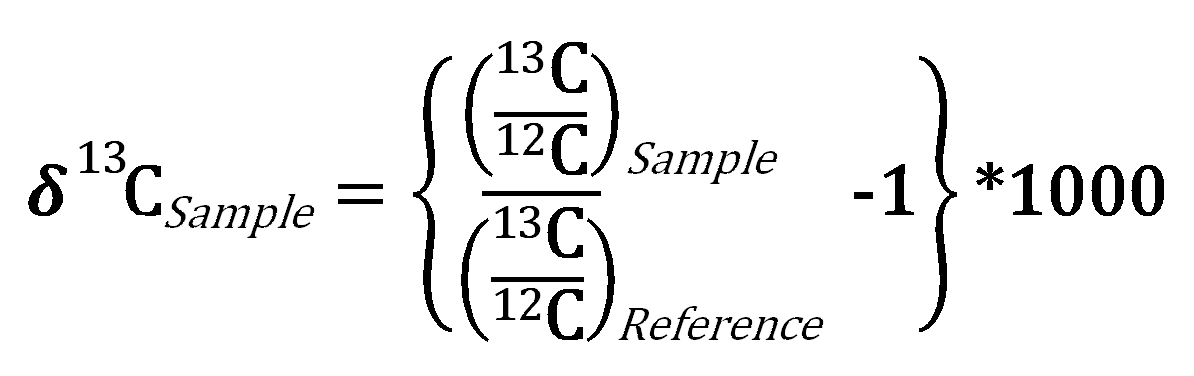
Carbon isotope ratios of soil organic matter under maize cultivation showed an increase in δ 13 c with time of cultivation table 7 the proportion of carbon originating from maize was calculated. Carbon isotope ratio measurements were made on soil organic matter and on doc with both extraction methods. Shown for reference are the average and 1 and 2 sigma range for the data published on these heinrich layers and reported compositions of potential source areas of ice rafted detritus grousset et al 2001 and references therein. This keyword data block is used to enable printing of isotopic ratios in species or phases to the output file.
What is an isotope. This type of analyzer is superior to the quadrupole type in this field of research for two reasons. The isotope ratios data block is used in the database file iso dat and is unlikely to be used in any. Carbon 12 is a stable isotope while carbon 14 is a radioactive isotope radioisotope.
A basic function defined in calculate values is used to calculate an isotope ratio which is then printed in the output file under the heading isotope ratios. For example an atom with 6 protons must be carbon and an atom with 92 protons must be uranium. Isotope ratio mass spectrometry. Stable isotope ratios are measured using mass spectrometry which separates the different isotopes of an element on the basis of their mass to charge ratio.
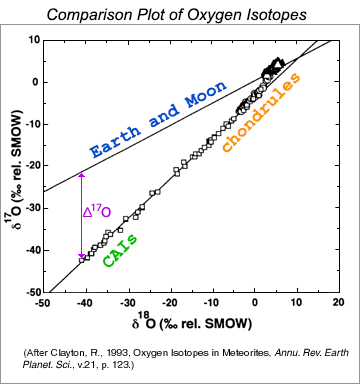
Nd sr isotope ratios of terrigenous clastic components of heinrich layers h1 h2 h4 and h5. A high accuracy high precision form of mass spectrometry used to determine ratios of atomic isotopes in small volumes of gas which are used in geochemistry cosmological chemistry carbon dating and tracer studies. Most instruments used for precise determination of isotope ratios are of the magnetic sector type. Elements are defined by the number of protons in the atomic nucleus.
Isotope definition any of two or more forms of a chemical element having the same number of protons in the nucleus or the same atomic number but having different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus or different atomic weights. This can be applied to a food web to make it possible to draw direct inferences regarding diet trophic level and subsistence isotope ratios are measured using mass spectrometry which separates the different isotopes of an element on the. Isotope analysis is the identification of isotopic signature the distribution of certain stable isotopes and chemical elements within chemical compounds.