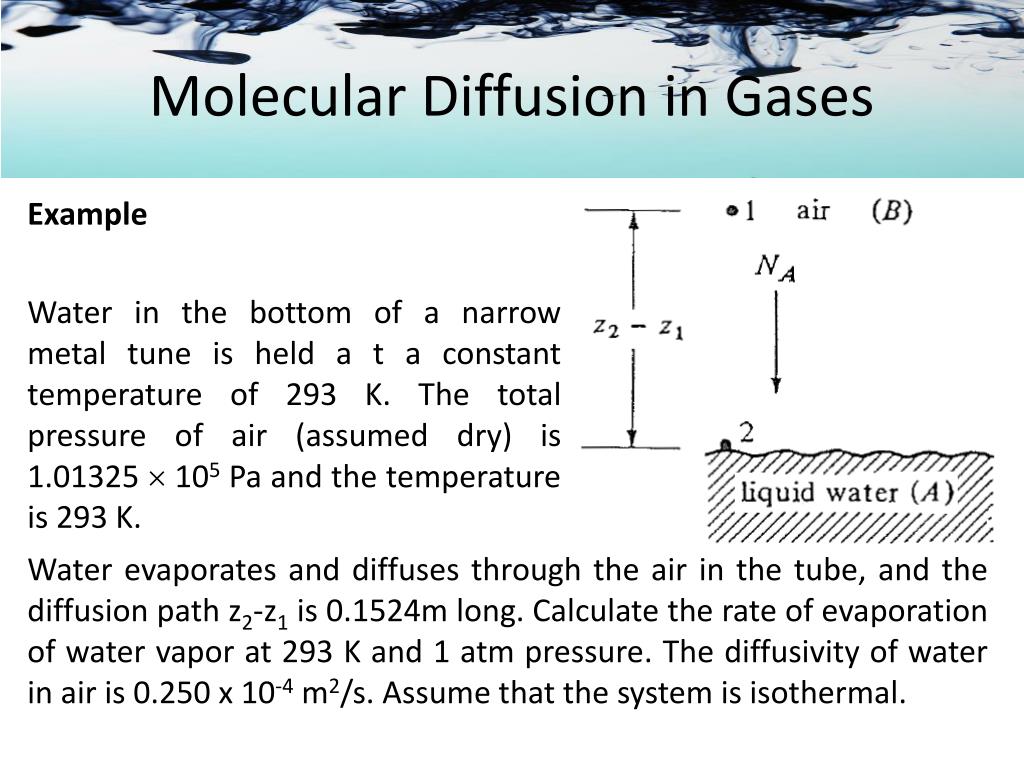
Definition Of Molecular Diffusion

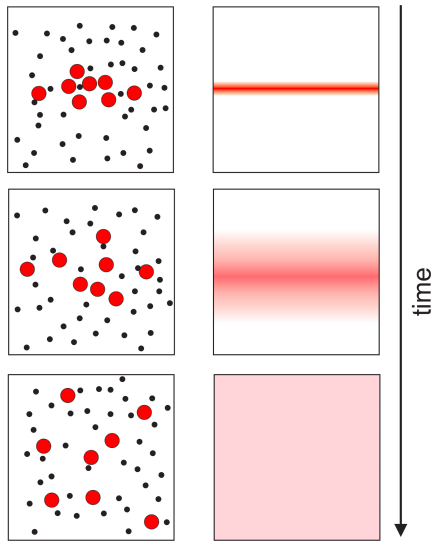
Diffusion is the net movement of anything for example atom ions molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
Definition of molecular diffusion. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in concentration. The concept of diffusion is widely used in many fields including physics particle diffusion chemistry biology sociology economics and finance diffusion of people ideas and price. The particles will mix until they are evenly distributed. Molecular diffusion often simply called diffusion is the thermal motion of all liquid or gas particles at temperatures above absolute zero the rate of this movement is a function of temperature viscosity of the fluid and the size mass of the particles.
Diffusion explains the net flux of molecules from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration but it is important to. The material that diffuses could be a solid liquid or gas. Diffusion is the movement of a fluid from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a high concentration region to a low concentration region.
Similarly the medium in which diffusion occurs could also be in one of the three physical states. Diffusion is a result of the kinetic properties of particles of matter. Diffusion happens in liquids and gases because their particles move randomly from. Diffusion explains the net flux of molecules from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration.
Molecular diffusion is the thermal motion of molecules at temperatures above absolute zero. Difference between molecular motion and diffusion definition. Molecular motion is the random movement of molecules in a substance without any applied external influence. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature viscosity of the fluid and the size and shape of the particles.
Diffusion is the movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.