Definition Of Neutron Diffusion

The neutron current is proportional to the net number of neutrons and is required in order to evaluate the movement of neutrons in or out of a specific volume.
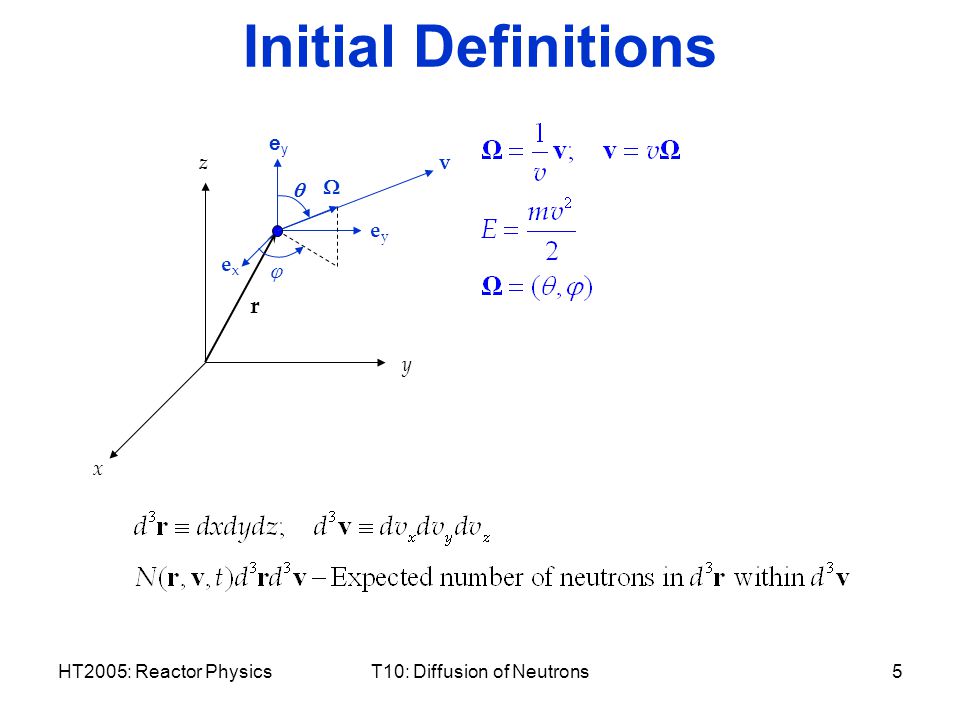
Definition of neutron diffusion. The derivation of the diffusion equation depends on fick s law which states that solute diffuses from high concentration to low but first we have to define a neutron flux and neutron current density the neutron flux is used to characterize the neutron distribution in the reactor and it is the main output of solutions of diffusion equations. 3 2 t d s 6 6 21 thus fick s law for neutron diffusion is given by. We define the diffusion coefficient. This is good material for graduate courses and as a means of providing a unified approach from which the many approximations can be derived.
We define the diffusion coefficient. The derivation of the diffusion equation depends on fick s law which states that solute diffuses from high concentration to low but first we have to define a neutron flux and neutron current density the neutron flux is used to characterize the neutron distribution in the reactor and it is the main output of solutions of diffusion equations. 3 2 t d s σ σ 21 thus fick s law for neutron diffusion is given by. Because diffusion is composed by a sum of different terms and if your temrs assorbtion and generation that describe the nuclear reaction are 0 there still a term that describe the neutron collision and this term involves the flick law so there still neutron diffusion also without nuclear reacion.
Transport theory provides the general transport equation or the boltzmann equation. The diffusion of neutrons 5 2 why diffusion movement of neutrons is similar to movement of gas particles. 22 it states that the current density vector is proportional to the negative gradient of the flux and establishes a relationship between them under the enunciated assumptions. One the flux is a scalar quantity which describes all of the path length s that neutrons traverse per unit.
Derivation of one group diffusion equation. J d ϕ 22 it states that the current density vector is proportional to the negative gradient of the flux and establishes a relationship between them under the enunciated assumptions. In other words φ and j are not allowed to show a jump.