Definition Of One Tailed Hypothesis

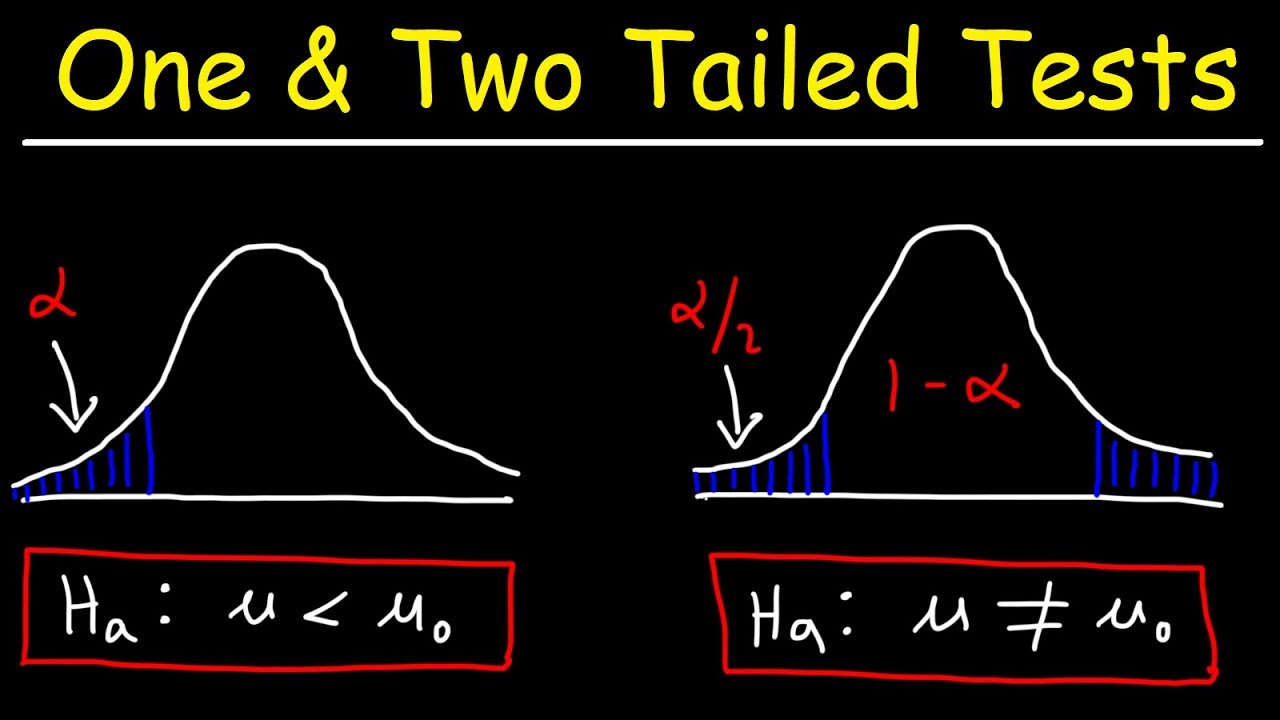
A one tailed test is a statistical hypothesis test set up to show that the sample mean would be higher or lower than the population mean but not both when using a one tailed test the analyst is.
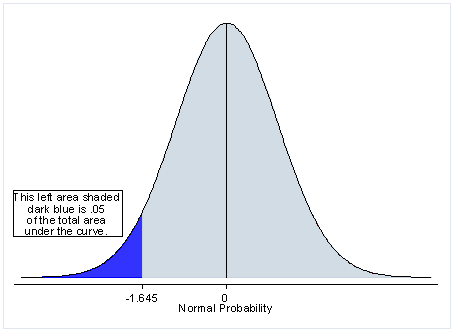
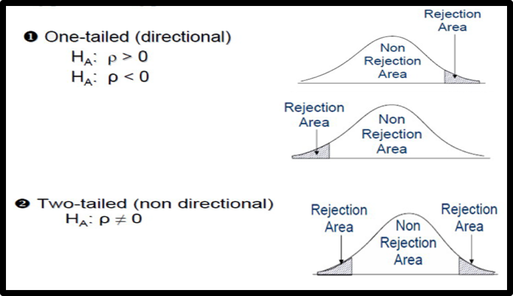
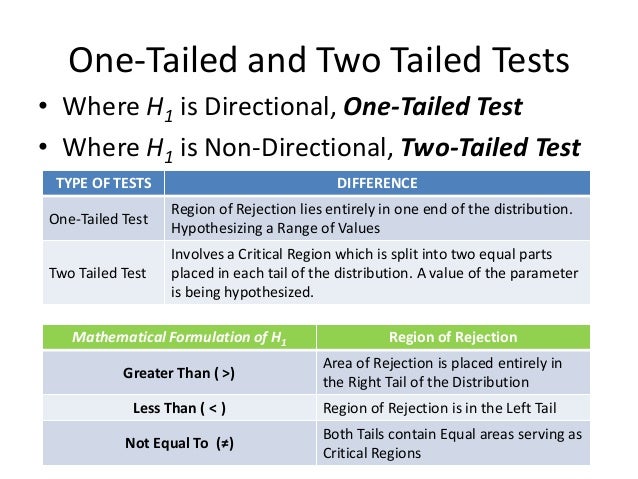
Definition of one tailed hypothesis. One tailed and two tailed test a one tailed test is a test in which the values of the parameter being studied in our previous example the mean cholesterol level under the alternative hypothesis are allowed to be either greater than or less than the values of the parameter under the null hypothesis but not both. This is a one tailed definition and the chi squared distribution is asymmetric only assuming positive or zero values and has only one tail the upper one. E g there will be a difference in how many numbers are correctly recalled by children and adults. The p value thus measures how likely the fit would be this bad or worse.
The one tailed test refers to a test of null hypothesis in which the alternative hypothesis is articulated directionally. However if the alternative hypothesis is not exhibited directionally then it is known as the two tailed test of the null hypothesis wherein the critical region is one both the tails. In statistics you compare a sample example. The statistical test of an experimental hypothesis wherein the predicted direction of an impact or union is occurs as ascertained.
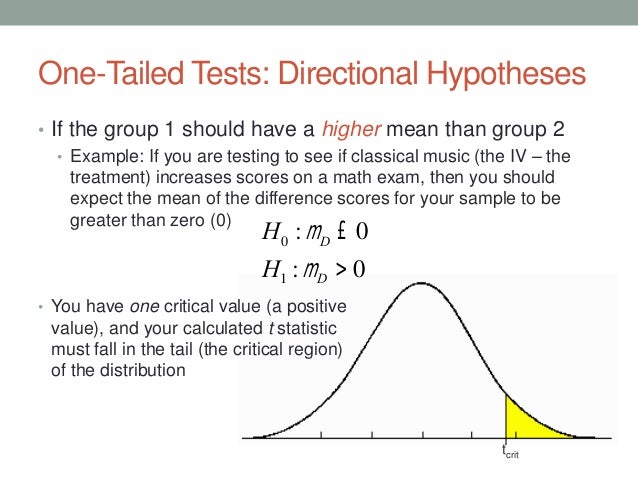
One tailed hypothesis tests are also known as directional and one sided tests because you can test for effects in only one direction. Psychology definition of one tailed test. One class of high school seniors sat scores and compare it to a larger set of numbers which is called a distribution the sat scores for all us high school seniors. A two tailed non directional hypothesis predicts that the independent variable will have an effect on the dependent variable but the direction of the effect is not specified.
One tailed hypothesis a one tailed hypothesis is used when you are interested in the determining the relationship between a sample and a distribution. When you perform a one tailed test the entire significance level percentage goes into the extreme end of one tail of the distribution. A one tailed hypothesis or directional hypothesis predicts the actual direction in which the findings will go it is more precise and usually used when other research has been carried out previously giving us a good idea of which way the results will go eg we predict more or less an increase or decrease higher or lowera two tailed hypothesis or non directional hypothesis predicts an. It measures goodness of fit of data with a theoretical distribution with zero corresponding to exact agreement with the theoretical distribution.