Historical Definition Of Hypothesis

Each hypothesis should clearly state the answer to the question followed by a why.
Historical definition of hypothesis. In science a hypothesis is an idea or explanation that you then test through study and experimentation. Scientists use the scientific method to study phenomenon they observe. The hypothesis being tested is exactly that set of possible probability distributions. Is something more than a wild guess but less than a well established theory.
The hypothesis plural hypotheses is a tentative solution. Solution of the problem or to seek. A hypothesis is something more than a wild guess but less than a well established theory. Emphasize that even in history detectives the experts first.
It contains both the argument and the main reasons in support of your argument. A hypothesis is a theory based on facts. A hypothesis is a single sentence answer to the key inquiry question that clearly states what your entire essay is going to argue. Hypothesis definition a proposition or set of propositions set forth as an explanation for the occurrence of some specified group of phenomena either asserted merely as a provisional conjecture to guide investigation working hypothesis or accepted as highly.
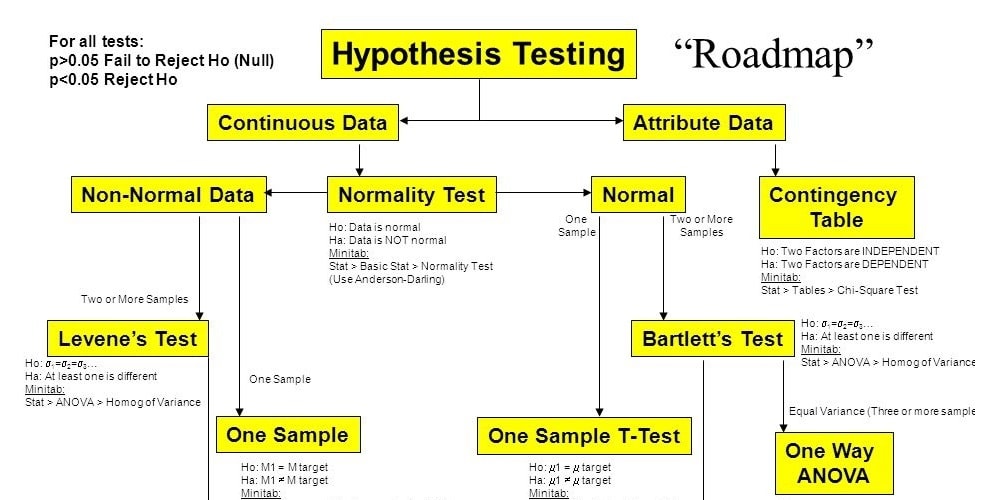
A hypothesis plural hypotheses is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon for a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis the scientific method requires that one can test it scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous observations that cannot satisfactorily be explained with the available scientific theories. First of all we need a historical hypothesis when our evidence is limited. Review with students various hypotheses that were created for the history detectives series. We picked up gencorp as a client jim lambert who was the vp of operations at allied signal went to gencorp as vp of operations and took us with him and we included the hypothesis testing flow chart in gencorp training.
A set of data or several sets of data taken together are modelled as being realised values of a collection of random variables having a joint probability distribution in some set of possible joint distributions. The research activities ar e planned to verify the hypothesis and not to find out the. A hypothesis is commonly known as an guess based on former knowledge or an educated guess. That is to say we infer from evidence and argumentation in order to establish a likely explanation for something that is open to question or interpretation.