Definition Of Differential Diffusion

If for every the matrix is positive definite then the operator is said to be elliptic.
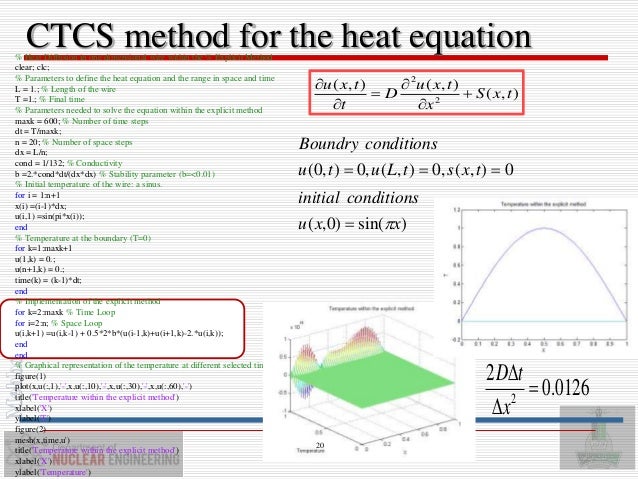
Definition of differential diffusion. In terms of the parameter ɛ νn 2 used frequently in oceanographic studies. Therefore in order to. How to use diffusion in a sentence. To solve the diffusion equation which is a second order partial differential equation throughout the reactor volume it is necessary to specify certain boundary conditions.
The action of diffusing. The diffusion equation is a parabolic partial differential equation in physics it describes the macroscopic behavior of many micro particles in brownian motion resulting from the random movements and collisions of the particles see fick s laws of diffusion in mathematics it is related to markov processes such as random walks and applied in many other fields such as materials science. It is very dependent on the complexity of certain problem. One of the simplest demonstrations of diffusion is adding a drop of food coloring to water.
For systems with more than two components the flow of any component and hence its d01719 depends on the concentration distribution of all components. Although other transport processes do occur diffusion is the key player. In this first lecture we introduce the main characters of this course. The conditions for differential diffusion are still uncertain however.
The differential equations 2 and 3 for the probability density are the fundamental analytic objects of study of diffusion processes. This is an important finding since the karlovitz numbers in the present datasets are located in the upper range of conventional si engine part load conditions. Examples of diffusion include the scent of perfume filling a whole room and the movement of small molecules across a cell membrane. Diffusion definition is the state of being spread out or transmitted especially by contact.
If u and l t are the velocity and length scales of the large eddies and n is the buoyancy frequency then effects of molecular diffusion should appear when both the froude number fr t u nl t and the reynolds number re t ul t ν are small. One dimensional problems solutions of diffusion equation contain two arbitrary constants. Cellular diffusion is the process that causes molecules to move in and out of a cell. Molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
A differential operator on is called a diffusion operator if it can be written where and are continuous functions on and if for every the matrix is a symmetric and nonnegative matrix. The limiting differential diffusion coefficient is the value of d i extrapolated to zero concentration of the diffusing species.