Definition Of Isotope In Biology
Elements are defined by the number of protons in the atomic nucleus.
Definition of isotope in biology. The mass of a neutron is almost identical to that of a. Different atomic forms of the same element are called isotopes of the element. Carbon 14 14 c is a naturally occurring radioisotope that is created in the atmosphere by cosmic rays this is a continuous process so more 14 c is always being created. Learn isotope definition in biology with explanation to study what is isotope.
The initial isotope is called the parent isotope while the atoms produced by the reaction are called daughter isotopes. Browse isotope explanation with biology terms to study for online university degree programs. Isotopes in the largest biology dictionary online. Isotope definition is any of two or more species of atoms of a chemical element with the same atomic number and nearly identical chemical behavior but with differing atomic mass or mass number and different physical properties.
In addition to protons the atoms of nearly every element also contain neutrons. There are 275 isotopes of the 81 stable elements in addition to over 800 radioactive isotopes and every element has known isotopic forms. Radiobiology one of several nuclides having the same number of protons in their nuclei and hence having the same atomic number but differing in the number of neutrons and therefore in the mass number. What is an isotope.
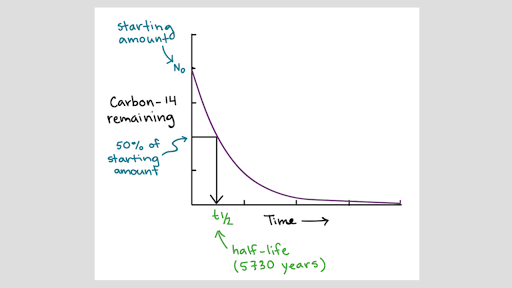
When an organism dies it is no longer ingesting 14 c so the ratio will decline. Isotope definition any of two or more forms of a chemical element having the same number of protons in the nucleus or the same atomic number but having different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus or different atomic weights. More than one type of daughter isotope may result. As an example when u 238 decays into th 234 the uranium atom is the parent isotope while the thorium atom is the daughter isotope.