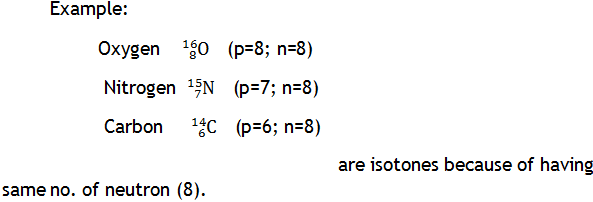Definition Of Isotopes And Isobars With Example
Therefore the atomic numbers are essentially different from each other.
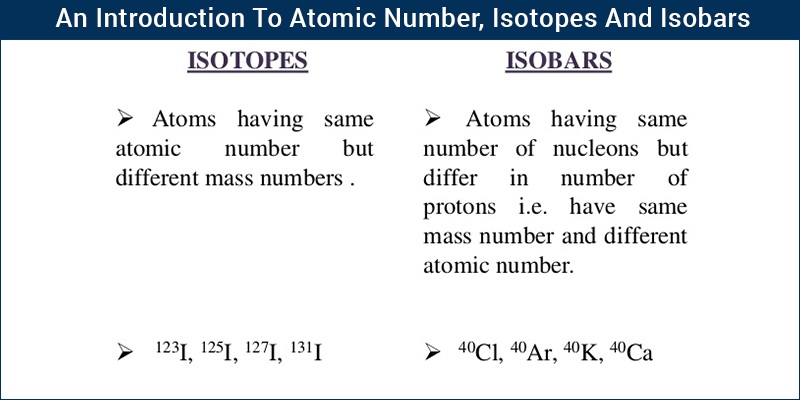
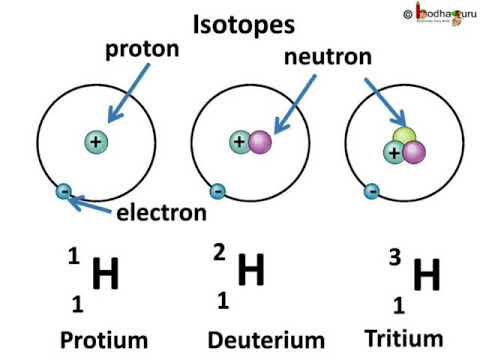
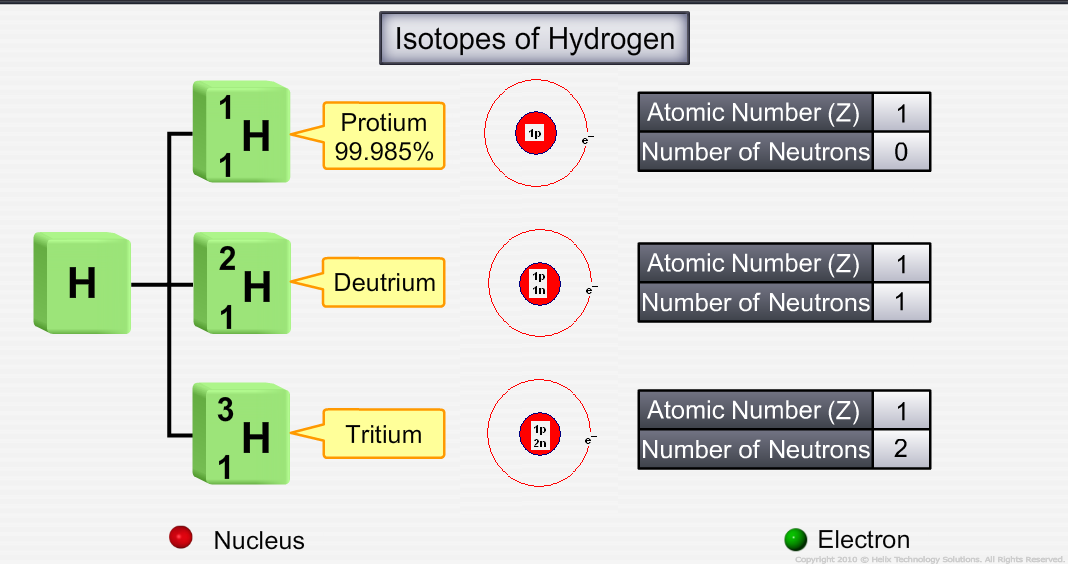
Definition of isotopes and isobars with example. Atomic numbers of isobars vary from each other. Examples of isotopes and isobars. These have the same atomic number one but different mass numbers 1 2 and 3. Hydrogen is the common example which has three isotopes.
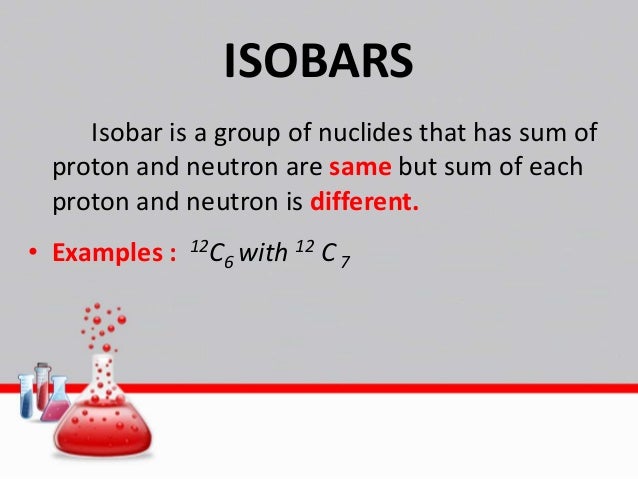
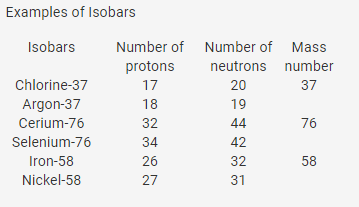
The atoms which posses same atomic number the atoms same element but different mass number are called isotopes. Isobars and element and the atomic mass of the isotope for example d isotopes definition and examples in isobar nuclear physics britannica com may 13th 2018 isobar isobar in nuclear. Isobars are different elements with a similarity. Species or atoms having same atomic mass number but different atomic number.
For example 14 6 c 6 14 c 14 7 n 7 14 n. Examples of isotopes and isobars. Examples of isotopes and isobars. Isobars are atoms of different chemical elements.
I 32 ce 76 34 se 76 ii 26 fe 58 27 ni 58 iii 18 ar 40 19 k 40 20 ca 40 iv 11 na 24 12 mg 24 v 27 co 64 28 ni 64. Isotopes are examples for differences within a single element. Isotopes are atoms of an element which have the same proton number but different nucleon numbers. They have the same number of nucleons i e sum of protons and neutrons are same but number of protons and neutrons alone varies between them.
Atomic numbers of all isotopic forms of a single element are equal. Example 14 6 c 6 14 c 15 7 n 7 15 n other examples includes boron 12 and carbon 13 nuclei both contain 7 neutrons and so are isotones. Isobars are different chemical elements having same atomic mass. Therefore isotopes of the same chemical element have the same atomic number but different atomic masses.
These three isotopes are commonly known as hydrogen or protium deuterium d and tritium t respectively. The atoms which posses different atomic number with same mass number are called isobars. Structure of the atom. The difference in mass number is due to different number of neutrons present in the nucleus.
Species having same number of neutrons but different number of protons are called isotones.