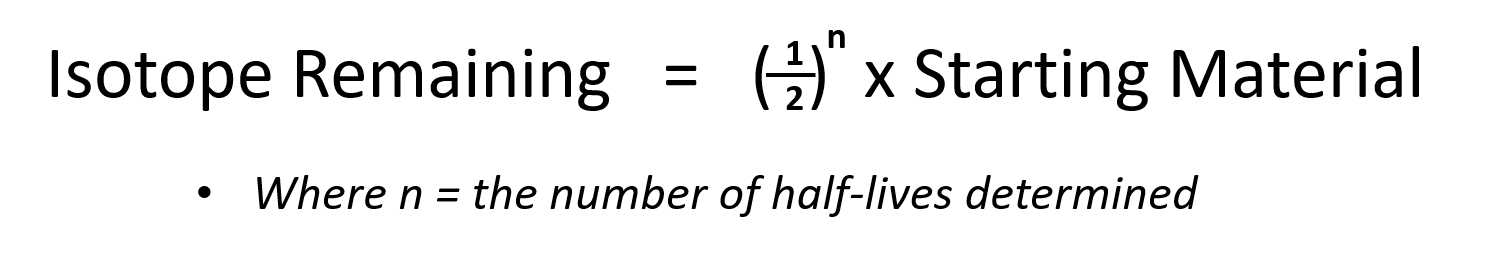Definition Of Radiation Isotope

Stable isotope one that does not transmute into another element with emission of.
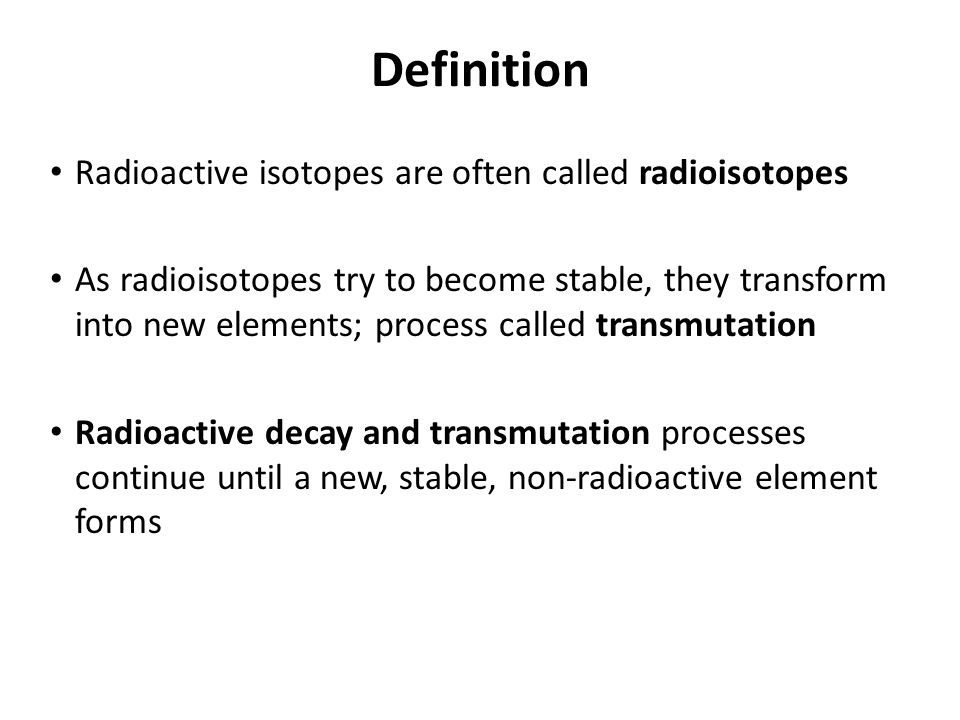
Definition of radiation isotope. I so tōp a chemical element having the same atomic number as another i e the same number of nuclear protons but having a different atomic mass i e a different number of nuclear neutrons. Isotope definition any of two or more forms of a chemical element having the same number of protons in the nucleus or the same atomic number but having different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus or different atomic weights. The nuclide concept referring to individual nuclear species emphasizes nuclear properties over chemical properties whereas the isotope concept grouping all atoms of each element emphasizes chemical over nuclear. Radioactive isotope radioisotope.
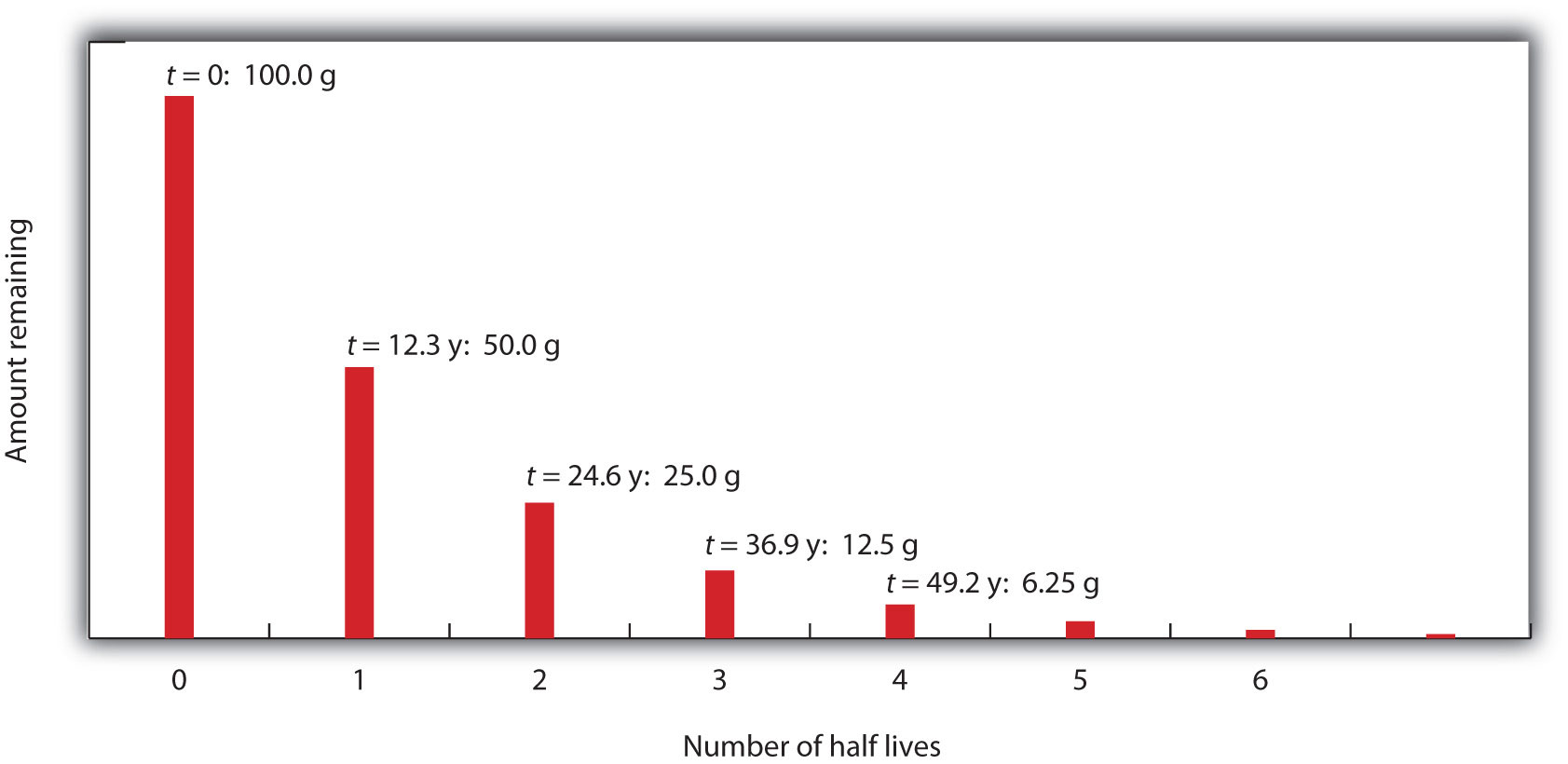
Atoms are made up of protons neutrons and electrons. 6 1 6 secondary ion mass spectrometry methods. Radiation dosimetry one of the most useful terms for estimating how quickly a nuclide will decay is the radioactive half life t1 2. The half life is defined as the amount of time it takes for a given isotope to lose half of its radioactivity.
Change the number of neutrons in an atom and it becomes an isotope change the number of electrons it becomes an ion. De groot in handbook of stable isotope analytical techniques 2009. Look it up now. A general description of sims techniques is given in volume i part 1 chapter 30 a recent review on the use of sims technique for measuring light stable isotopes including o isotopes on silicate samples was presented by valley et al.
Every chemical element has one or more radioactive isotopes. There are 275 isotopes of the 81 stable elements in addition to over 800 radioactive isotopes and every element has known isotopic forms. Identifying the isotope will determine the energy penetrating ability of the radiation and radiation safety measures identifying the amount of radiation will determine radiation safety measures for responders and the public types of ionizing radiation of interest during a radiation incident alpha particles. Carbon 12 and carbon 14 are both isotopes of carbon one with 6 neutrons and one with 8 neutrons both with 6 protons.