Proper Definition Of Isotope

Every chemical element has one or more isotopes.
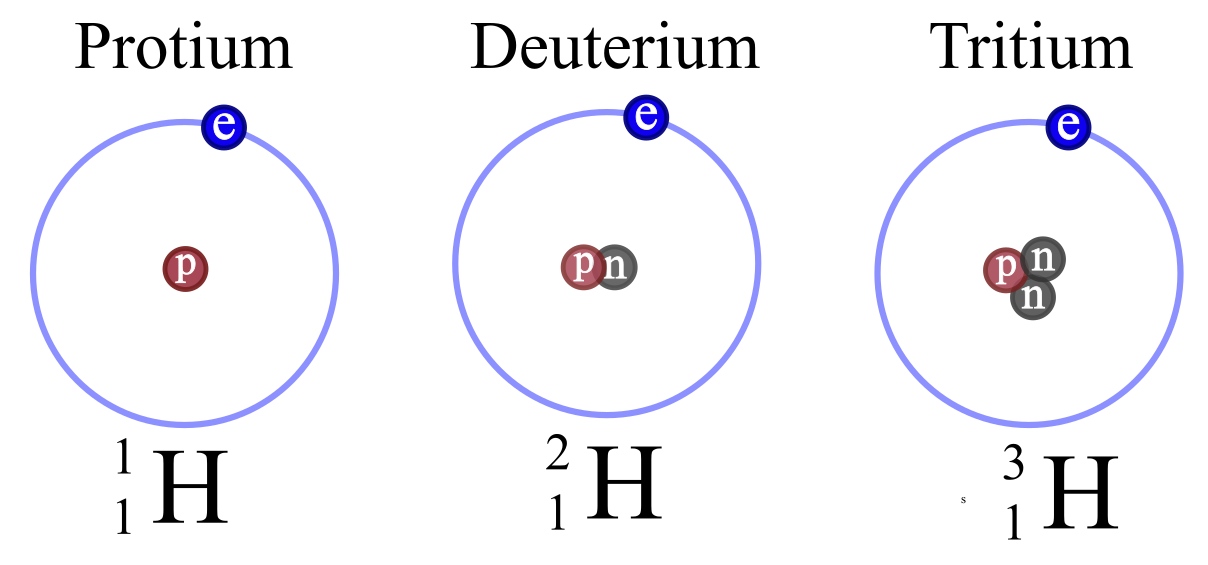
Proper definition of isotope. Atoms of an element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. Atoms that spontaneously emit radiation. An isotope is a variant of an element in which it has an equal number or protons but a varied number of neutrons. Hydrogen is the common example which has three isotopes these have the same atomic number one but different mass numbers 1 2 and 3.
Carbon 12 is a stable isotope while carbon 14 is a radioactive isotope radioisotope. Sodium 23 and sodium 24 are known as isotopes of sodium. Group of answer choices. Atoms in which the number of protons is different from the number of neutrons.
Isotopes are atoms of an element which have the same proton number but different nucleon numbers. Atoms with a mass number greater than the atomic number. Write the proper isotopic symbol including atomic number mass number for each of the following. What is the proper definition of an isotope.
Atoms that spontaneously emit radiation. The notation of an isotope occurs by adding a subscipt and superscript to the left side of an element such as 238 92u uranium isotope. Atoms with a mass number greater than the atomic number. What is the definition of an isotope.
What is the proper definition of an isotope. Carbon 12 and carbon 14 are both isotopes of carbon one with 6 neutrons and one with 8 neutrons both with 6 protons. A helium 3 b nitrogen 13 c molybdenum. Isotope one of two or more species of atoms of a chemical element with the same atomic number and position in the periodic table and nearly identical chemical behaviour but with different atomic masses and physical properties.
Group of answer choices. However with proper calibration variability in individual aa incorporation rates may also provide a framework to create an isotopic clock as has been done previously by comparing bulk isotope values of multiple tissues with different incorporation rates to determine the length of time an individual has spent on a new resource e g habitat.