Definition Of Gene Silencing In Biology

A mechanism by which cells shut down large sections of chromosomal dna.
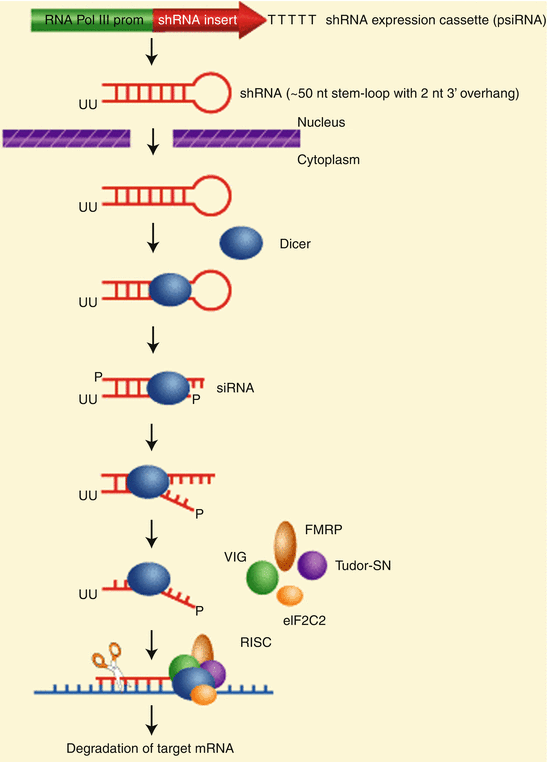
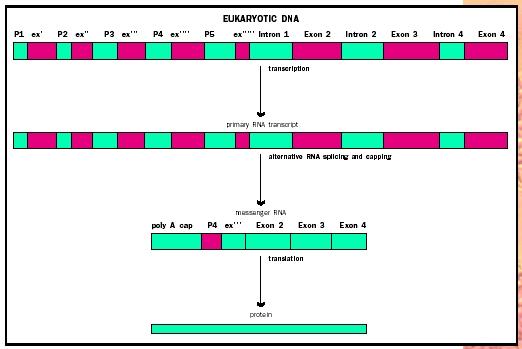
Definition of gene silencing in biology. Gene silencing the inhibition of transcription of a gene. The definition is it is a process from the genetics wherein the gene expression is reduced when gene regulation occurs through inhibition of transmission transcription of genetic information dna to mrna transcriptional gene silencing or the subsequent protein synthesis translation stored on the mrna information into a protein post transcriptional gene. Dna methylation is an important cause of gene silencing and when this affects tumour suppressor genes may be a cause of cancer gene silencing a therapeutic technique to prevent the expression of genes that are acting harmfully. It is generally used to describe the switching off of a gene by a mechanism other than genetic modification.
In particular methods used to silence genes are being increasingly used to produce therapeutics to combat cancer and other diseases such as infectious diseases and neurodegenerative disorders. Gene silencing is done by incorporating the dna to be silenced into a form of dna called heterochromatin that is already silent. Gene silencing can occur during either transcription or translation and is often used in research. Gene silencing is the process of turning off a gene thereby preventing it from expressing in the form of protein production or other forms of expression.
Gene silencing is the regulation of gene expression in a cell to prevent the expression of a certain gene. Double stranded rna molecules introduced into cells with viral. In eukaryotes a wide range of biological processes are regulated through gene silencing including development organ formation and stress responses. Gene silencing definition a genetic engineering technique in which researchers prevent the expression of a particular gene by using small interfering rnas sirnas or micrornas mirnas to interfere with translation.
This process happens naturally in many cases for the purpose of regulating the expression of genes and preventing potential damage from viruses. Gene silencing refers to a mechanism by which cells shut down large sections of chromosomal dna. Gene silencing also known as rna interference is a sequence specific gene inactivation system that downregulates rna accumulation at the transcriptional or post transcriptional levels.