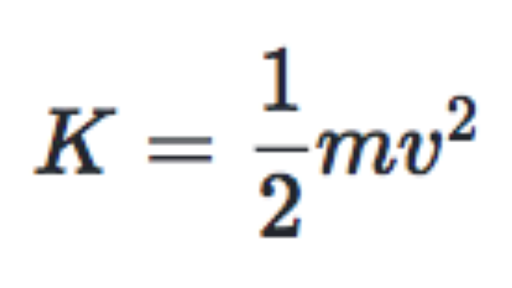Definition Of Temperature In Terms Of Kinetic Energy

Most thermometers rely on some characteristic of thermal expansion in order to function.
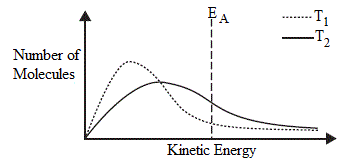
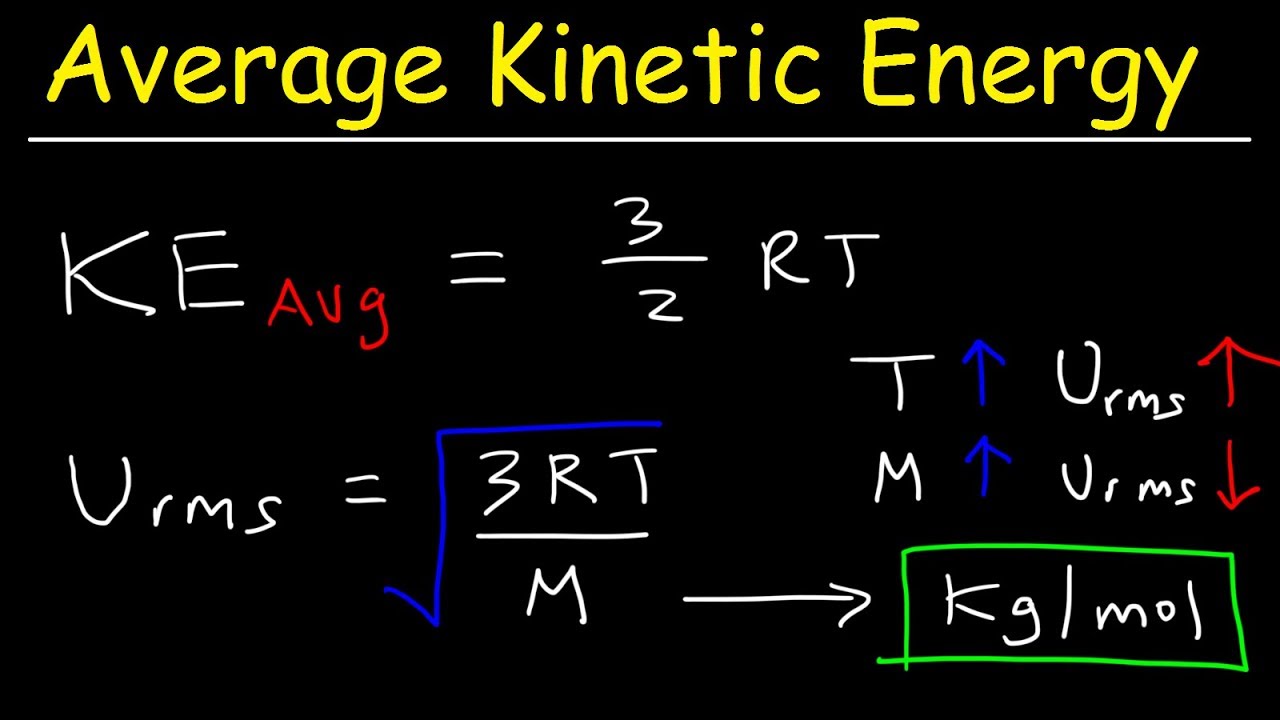
Definition of temperature in terms of kinetic energy. Clearly temperature has to do with the kinetic energy of the molecules and if the molecules act like independent point masses then we could define temperature in terms of the average translational kinetic energy of the molecules the so called kinetic temperature. The average kinetic energy of particles in a substance is referred to as temperature. These are actually relative terms. Define temperature in terms of ke.
Temperature determines the statistical occupation of the microstates of the ensemble. The reverse is usually done. The kinetic theory explains. The average kinetic energy of the molecules of an object is an important.
Save as pdf page id 52322. The microscopic definition of temperature is only meaningful in the thermodynamic limit meaning for large ensembles of states or particles to fulfill the requirements of the statistical model. This is roughly described by the kinetic theory at least for gases and fluids. Energy of motion is called kinetic energy.
Kinetic energy and temperature last updated. Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold something is. When the molecules move or vibrate more they have a higher kinetic energy and this is recorded as an increase in temperature. The instrument we use to measure temperature is the thermometer.
The faster the particles are moving the higher the temperature. Temperature is a measure of the internal energy of a system while heat is a measure of how energy is transferred from one system or body to another or how temperatures in one system are raised or lowered by interaction with another. The temperature of a body is proportional the the average kinetic energy of the particles molecules or atoms that make up the. Heat energy is the total kinetic energy of particles in a substance.
Temperature can be measured in degrees celsius c degrees fahrenheit f or kelvin. Boiling water is hot compared to ice but cold compared to the temperature of the sun s surface. For example 1 kg of iron has less heat energy than 1 kg of wood at the same temperature. It may well take different amounts of energy to get particles moving at the same.