Definition Of Magnetic Force For Class 8
Donate or volunteer today.
Definition of magnetic force for class 8. A current carrying conductor experiences magnetic forces in a magnetic field. Our mission is to provide a free world class education to anyone anywhere. Figure 8 3 4 a curved wire carrying a current i. Khan academy is a 501 c 3 nonprofit organization.
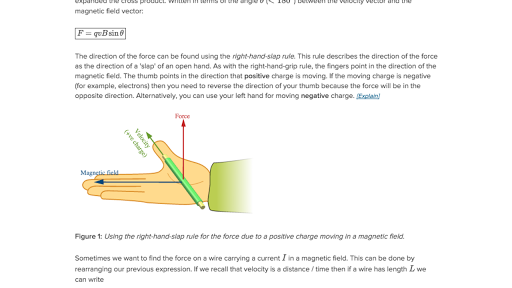
Magnetic force on a current carrying wire. Fleming s left hand rule predicts the direction of the magnetic forces f ilbsinθ. The inner core is solid iron as a simple. University and has many.
Magnetic field created by a current. Force and pressure class 8 science chapter 11 as per ncert book used in cbse and other schools. It is the force exerted by magnets on iron objects. 8 3 3 the magnetic force on the wire is given by.
It is the basic force responsible for such effects as the action of electric motors and the attraction of magnets for iron. Class 8 force and pressure tagged with. The force exerted between. Ii living and non living things can apply force.
We can define force as the push or pull of an object. Where a and b represent the endpoints of the wire. Force is everywhere and it comes in a variety of sizes directions and type. The lesson covers the complete explanation of class 8 chapter 11 force and pressure.
Electrostatic force example of non contact force gravitational force magnet magnetic force non contact force about mrs shilpi nagpal author of this website mrs shilpi nagpal is msc hons chemistry and bsc hons chemistry from delhi university b ed i. The earth s magnetic field with a magnetic dipole moment of 8 2 x 10 22 a m 2 is generated by currents within the molten iron of the earth s outer core. The force exerted between a magnet and a moving electrically charged particle. The force exerted between magnets.
One which applied force the other which receive force. I force is a push or a pull. Learn more about the magnetic force in this article. Learn force definition unit types of force with solved examples.
Magnetic force attraction or repulsion that arises between electrically charged particles because of their motion. As an example consider a curved wire carrying a current i in a uniform magnetic field b g as shown in figure 8 3 4. Where f is the magnetic force i is current l is the length of a straight conductor in a uniform magnetic field b and θ is the angle between i and b. Iii to apply a force over an object interaction between object and source of force is necessary.
Topics covered are force and types of force fluids and fluids pressure.