Definition Of Diffusion In Chemistry Class 9

The phenomenon of mixing of particles of different substances together is known as diffusion.
Definition of diffusion in chemistry class 9. The transport of matter continues until equilibrium is reached and there is a uniform concentration through the material. List the types of diffusion. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration down the concentration gradient. Diffusion is the net movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
Diffusion is the net movement of anything for example atom ions molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion takes place because of the movement of particles of matters. The rate of diffusion increases on increasing the temperature of the diffusing substance. Diffusion can be described as the random movement of particles through space usually due to a concentration gradient.
The mixing of different gases in air is a natural process that takes place continuously. Diffusion is the movement of atoms ions or molecules from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in concentration. Diffusion is a result of the kinetic properties of particles of matter.
In this video follwoing sub topics have been. Diffusion is fastest in gases and slowest in solids. Diffusion occurs in gases liquids and solids. The particles will mix until they are evenly distributed.
Topic 5 3 liquid state. Diffusion may also be thought of as the movement of particles down a concentration gradient. The material that diffuses could be a solid liquid or gas. Diffusion is a physical process that refers to the net movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to one of lower concentration.
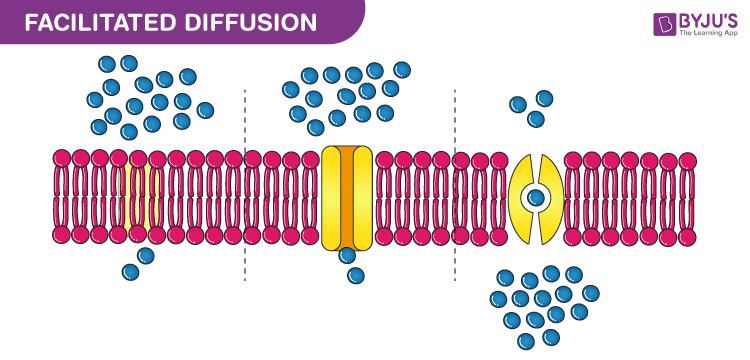
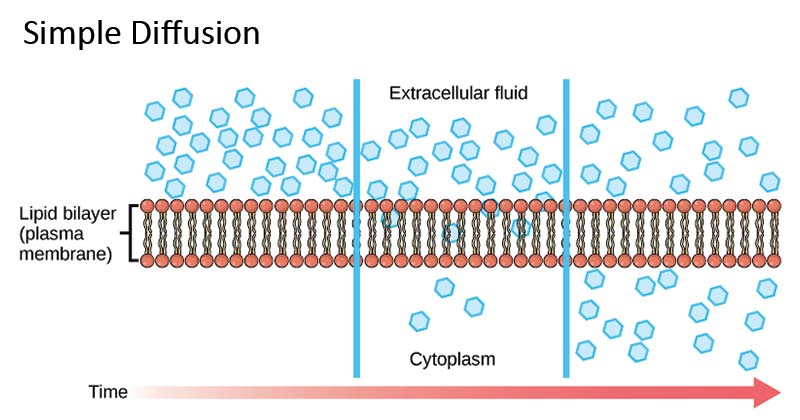
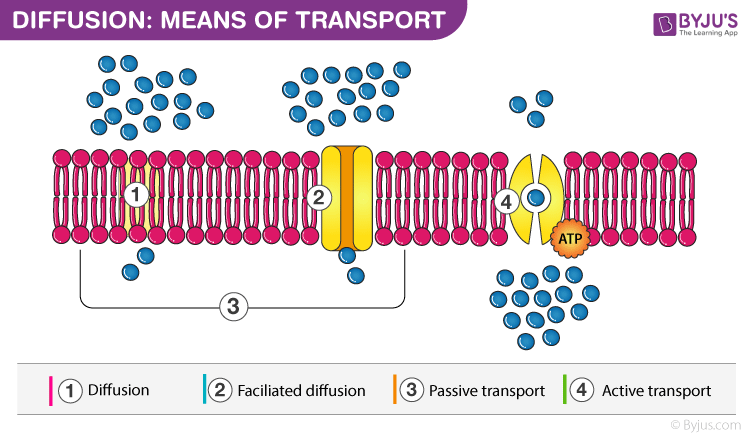
Similarly the medium in which diffusion occurs could also be in one of the three physical states. Diffusion can be divided into two main types namely simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. The diffusion coefficient d can be solved for with fick s laws of diffusion which are broken up into two laws. Diffusion is the movement of a fluid from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Diffusion is a spontaneous process and is a result of the random thermal motions between two particles.